Xiaomi
New Xiaomi Pad 7 Featuring High-End Chipsets to Arrive in February

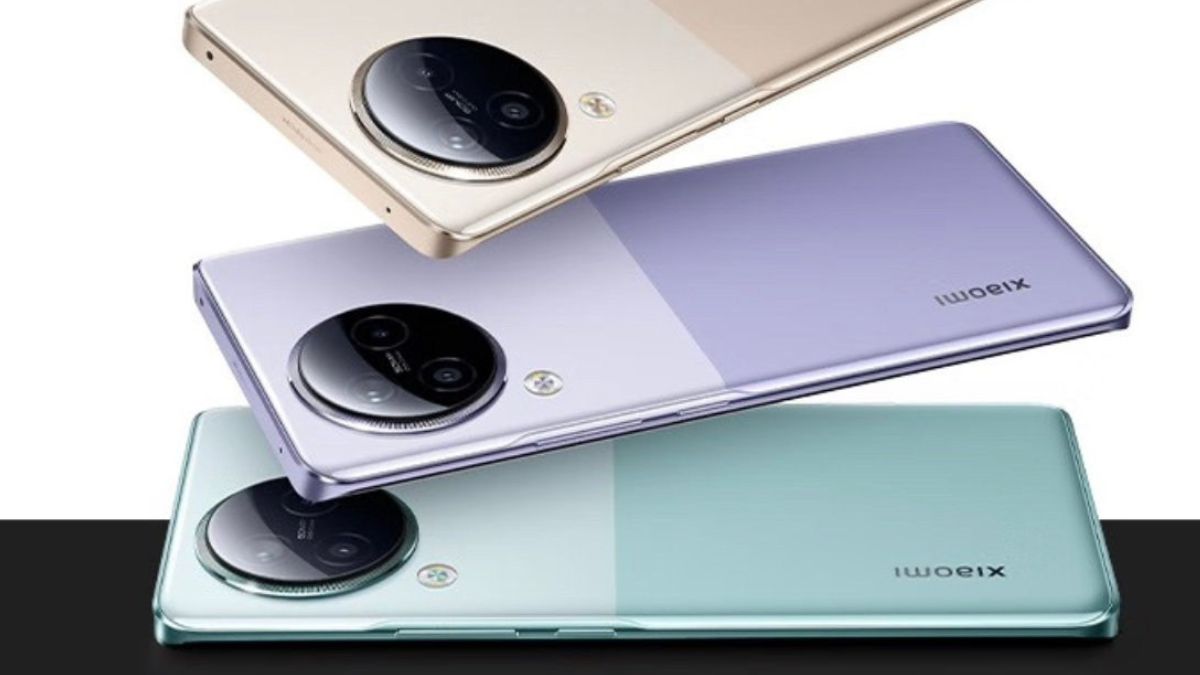
In April 2023, Xiaomi launched the Pad 6 Pro in China and is now gearing up for the release of its highly anticipated “Xiaomi Pad 7 lineup.” According to reliable sources, the new flagship tablet is launching next month, and it will have a Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 chipset.
The leak hints at a Pad 7 model equipped with last year’s Snapdragon 8 Gen 2, while the Pro variant is expected to feature Qualcomm’s latest top-tier SoC. This marks a significant improvement from the previous Pad 6 lineup, where the Pro and Max models were equipped with a one-year-old chip, while the vanilla version, reviewed last summer, housed a dated Snapdragon 870.
The Pad 7 might support 100W fast charging and the Pad 7 Pro is rumored to sport an OLED panel, a first move for Xiaomi’s tablet series, which has traditionally featured LCD displays.
While these features are certainly appealing, fans are hoping that Xiaomi will break its trend of limiting top-tier tablets to the Chinese market. Many enthusiasts are eagerly anticipating the global release of the Pad 7 Pro, with its advanced features and top-of-the-line specifications.
For More Such Updates Follow Us On – Telegram, Twitter, Google News, WhatsApp and Facebook
News
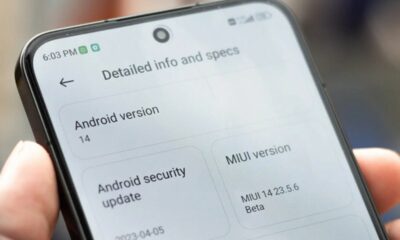
POCO F5 Receives HyperOS Update Rollout Across India

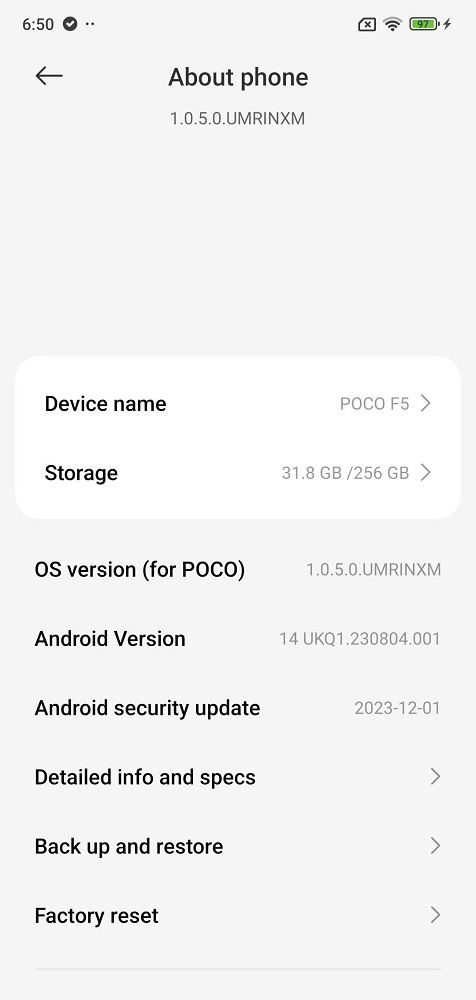
POCO has officially announced the widespread rollout of the HyperOS update for its POCO F5 smartphone in India. This comes a month after the initial confirmation and follows a successful pilot rollout in the preceding weeks. Xiaomi’s HyperOS is a human-centric system designed to connect personal devices, cars, and smart home products.
The primary focus of HyperOS lies in ensuring the best device performance, facilitating convenient connections across various platforms, and prioritizing end-to-end privacy and security.
The Xiaomi 13 Pro also has a HyperOS update with version 1.0.5.0.UMRINXM comes with the size of 5GB. The HyperOS update brings the Android security patch for December 2023.
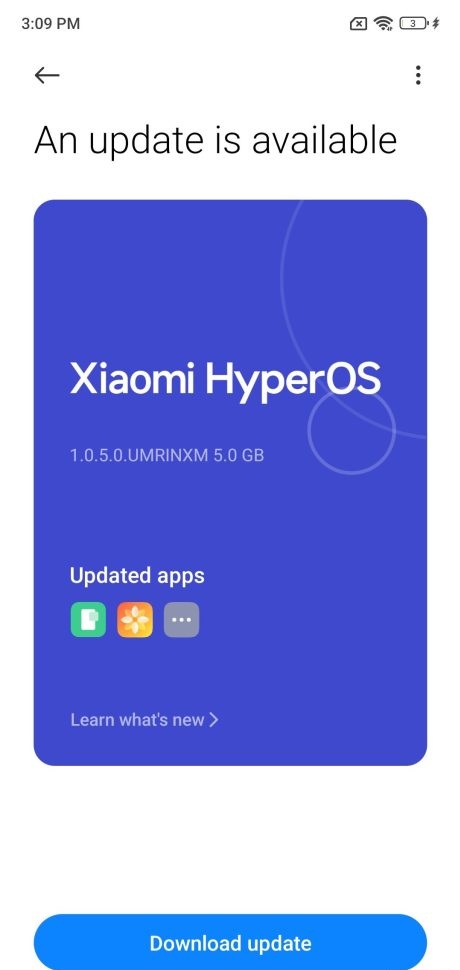
Changelog:
System
- Updated Android Security Patch to December 2023. Increased system security.
Comprehensive refactoring
- Upgraded memory management engine makes frees up more resources and makes memory usage more efficient
Vibrant aesthetics
- Global aesthetics draw inspiration from life itself and change the way your device looks and feels.
New animation language makes interactions with your device wholesome and intuitive.
Natural colors bring vibrancy and vitality to every corner of your device.
Our all-new system font supports multiple writing systems.
Redesigned Weather app not only gives you important information, but also shows you how it feels outside.
Notifications are focused on important information, presenting it to you in the most efficient way
Every photo can look like an art poster on your Lock screen, enhanced by multiple effects and dynamic rendering.
New Home screen icons refresh familiar items with new shapes and colors
Our in-house multi-rendering technology makes visuals delicate and comfortable across the whole system.
Multitasking is now even more straightforward and convenient with an upgraded multi-window interface.
Other improvements and optimization
- New: VoNR support for Jio
Users can expect improved performance, seamless connectivity, and enhanced security features as they launch the HyperOS on their POCO F5 smartphones.
For More Such Updates Follow Us On – Telegram, Twitter, Google News, WhatsApp and Facebook
News
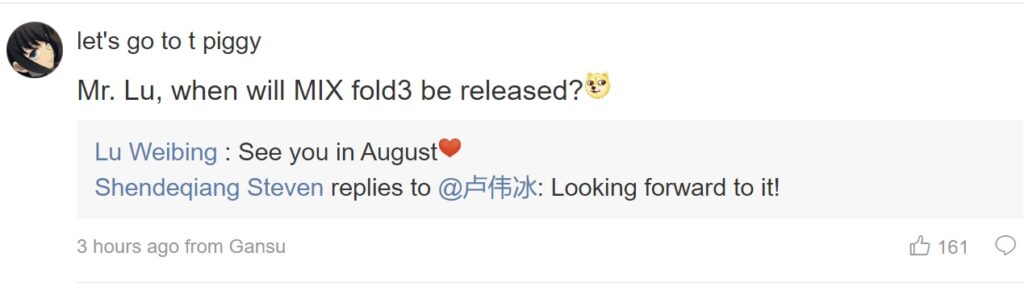
Xiaomi President Confirms Arrival of Xiaomi MIX Fold 3 with August 2023 Launch
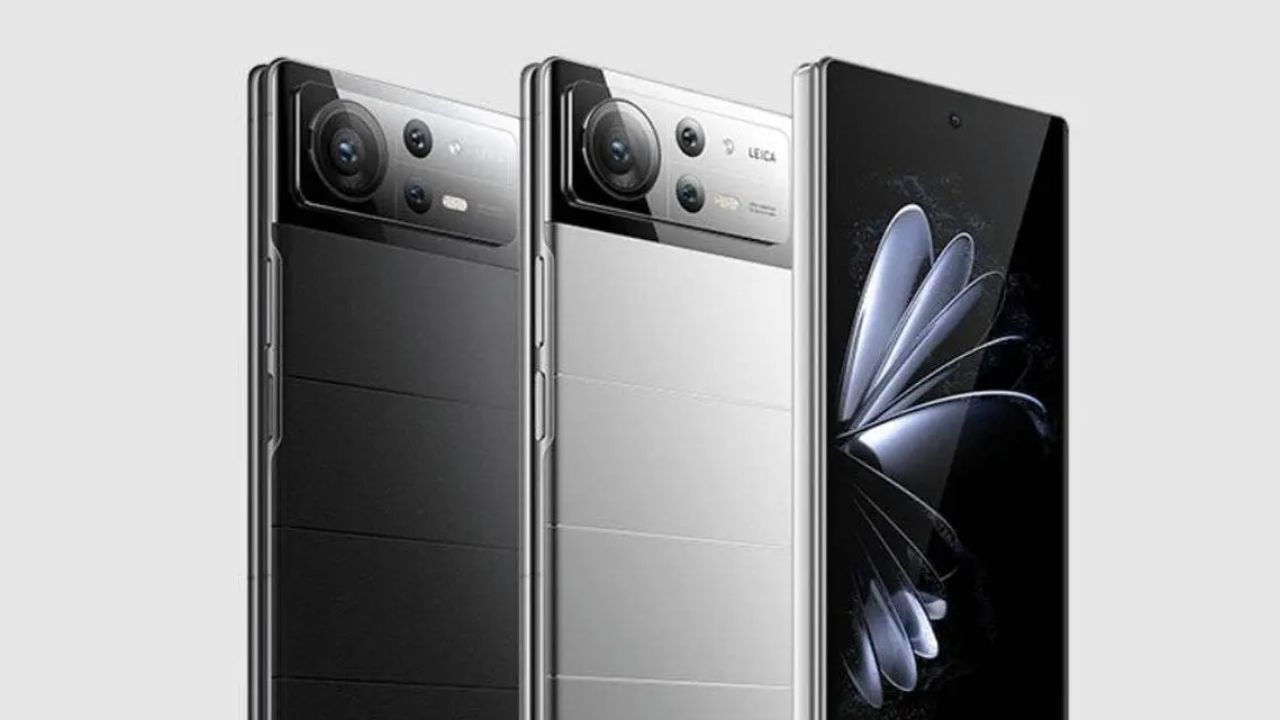

Xiaomi enthusiasts around the world are eagerly awaiting the arrival of the Xiaomi MIX Fold 3, the next-generation foldable smartphone from the Chinese tech giant. With an expected launch date in August 2023, this highly anticipated device is set to redefine the boundaries of mobile technology with its innovative features and cutting-edge design.
The news of the upcoming Xiaomi MIX Fold 3 was revealed by none other than the president of Xiaomi, Lu Weibing. During the launch event of the Xiaomi Smart Manufacturing Digital Intelligence System 2.0 at the Beijing Yizhuang Smart Factory, Lu made an exciting announcement that the first mass-produced model of this revolutionary smartphone will indeed be the Xiaomi MIX Fold 3.
This announcement has sparked a wave of speculation and excitement among tech enthusiasts and Xiaomi fans alike. With the confirmation of the MIX Fold 3’s existence and imminent launch, anticipation is building as users eagerly await the unveiling of this groundbreaking device.
Rumors surrounding the specifications of the Xiaomi MIX Fold 3 suggest that it will boast an impressive array of features. The device is expected to sport a large foldable display, offering users a truly immersive and unique viewing experience. The camera setup is also rumored to be exceptional, with a 50 MP Sony IMX 858 sensor, a telephoto lens, and a periscope telephoto lens that mirrors the setup found in the Xiaomi 13 Ultra.
With the MIX Fold 3, Xiaomi aims to build upon the success of its previous foldable smartphones, taking the technology to new heights. The company has a reputation for delivering top-notch devices that offer a combination of style, functionality, and affordability, and the MIX Fold 3 is poised to continue this tradition.
As August 2023 approaches, tech enthusiasts and smartphone aficionados will be eagerly awaiting the official launch of the Xiaomi MIX Fold 3. The device promises to deliver an unrivaled user experience and push the boundaries of what a smartphone can do. With its innovative features and cutting-edge design, the MIX Fold 3 is set to make a significant impact in the competitive smartphone market, further solidifying Xiaomi’s position as a leading player in the industry.
For More Such Updates Follow Us On – Telegram, Twitter, Google News, WhatsApp and Facebook
News
Xiaomi 12 Lite Joins Android 14 Testing for MIUI 15: Stable Update Expected in Q1 2024
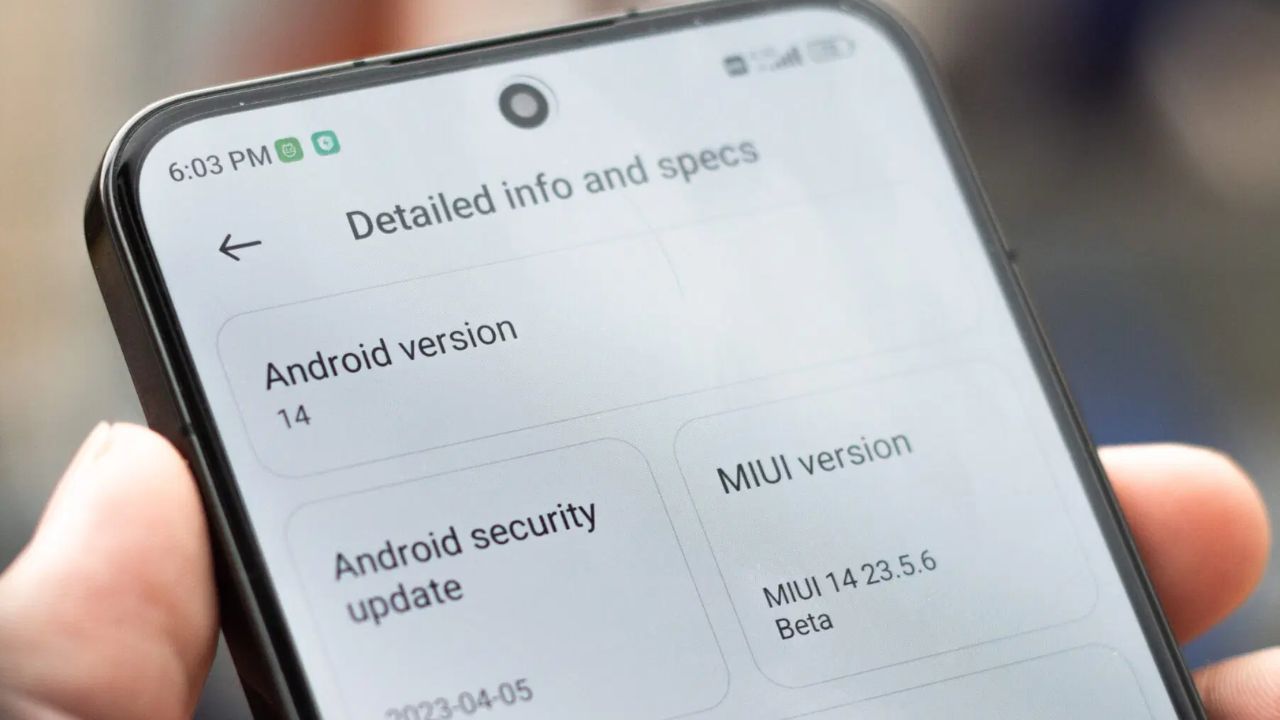
Xiaomi, the renowned Chinese smartphone manufacturer, has commenced testing its highly anticipated MIUI 15 update for Xiaomi phones. The company has recently included another popular Xiaomi phone in the testing phase for Android 14 compatibility, bringing users one step closer to receiving the MIUI 15 update. In the meantime, leaked pre-builds of MIUI 15 have already surfaced, generating excitement among Xiaomi enthusiasts.
Among the devices selected for Android 14 testing are the Mi 11, Redmi K60, and Xiaomi 13 Ultra, along with several others. These devices are expected to receive a stable Android 14 update along with an upgraded MIUI version in early 2024. Users can anticipate the release of the MIUI 15 update in the upcoming months following the launch of the Xiaomi 14 series, which is scheduled for November.
Xiaomiui, a reputable source for Xiaomi-related news, has reported that Xiaomi initiated Android 14 testing for the Xiaomi 12 Lite through the China beta version 23.7.1. It is speculated that the new update will be based on MIUI 15, with a stable version projected to be available by February 2024.
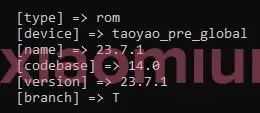
Providing further evidence of Xiaomi’s progress, a screenshot from Xiaomiui showcases the Xiaomi 12 Lite being used in the internal testing for Android 14. Users can anticipate a stable update in the first quarter of 2024, which will be built upon the MIUI 15 framework.
The upcoming MIUI 15 update is expected to introduce a range of new features and enhancements to enhance the user experience on Xiaomi devices. Xiaomi has consistently strived to deliver regular updates and improvements to its MIUI software, ensuring that users receive the latest advancements and security patches.
As Xiaomi continues to push the boundaries of smartphone technology, the anticipation for the MIUI 15 update builds among Xiaomi users. With Android 14 compatibility being tested on multiple devices and the imminent release of the Xiaomi 14 series, Xiaomi enthusiasts can look forward to a year of exciting updates and innovative features.
For More Such Updates Follow Us On – Telegram, Twitter, Google News, WhatsApp and Facebook